Q: I will be hunting with my two boys and would like to teach them the best way of identifying poisonous plants. Can you help?
A: There is no one rule for identifying poisonous plants. The most common culprits are poison ivy, poison oak and poison sumac, which are abundant in the Lower 48 and cause allergic skin reactions in millions each year. Plant structure varies by region and season. The plants are toxic year-round and release a potent antigen, the oil urushiol, when damaged. Once oil binds to skin proteins, contact dermatitis occurs as an itchy red rash with bumps or blisters. Wash away toxic oils after contact. Any left on your hands spreads the rash to wherever you touch as does contact with contaminated objects.
Poison Ivy: This is a trailing or climbing vine that grows as a short plant if it has no climbing support. It has three pointed leaflets, hence the saying, “Leaves of three, let them be.” However, leaves are not always uniform—which helps them blend in with nonpoisonous look-alikes—and appear reddish in spring, green in summer and yellow, orange or red in fall. Green flowers grow in the spring and are replaced by white berries. The stem hairs are arial roots that can also cause the infamous rash.
Poison Oak: This is a shrub with three to seven lobed leaflets and hairy undersides. Most common in the Southeast and Pacific Northwest, it has yellow-green flowers, and green or white berry clusters.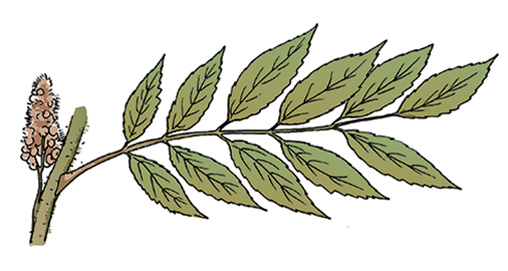
Poison Sumac: This grows as a shrub in the east with smooth leaflets and cream-colored drooping berries. The “leaves of three” rule is no help as sumac has seven to 13 leaves per branch, not three per cluster.



































